AI Act
The Artificial Intelligence (AI) Act has been in force since August 1, 2024 and will gradually come into effect over time. As a new legal milestone, the AI Act brings with it requirements for the use of artificial intelligence in companies in order to promote the responsible development and use of artificial intelligence in the EU. But instead of seeing only hurdles in the risk-based approach of the AI-Act, it also opens up a wide range of opportunities for a future-oriented AI strategy for companies.
In our newsletter, we take a first glance at the new legal framework and its significance for your company. We also show how companies can use legal compliance strategically to gain a competitive edge and promote innovative business models.
AI Act Insight: Ensuring Responsible AI for Your Business
The EU’s AI Act is here! Learn how this groundbreaking regulation impacts your business. We’ll break down the risk-based approach to AI systems, focusing on high-risk applications and compliance requirements. Discover practical steps to ensure transparency and leverage tools like AI-Marts for effective AI governance.
What is the AI Act and Why Should You Care?
The AI Act aims to make the use of artificial intelligence within the EU safer and more trustworthy by creating clear rules for the development and use of AI systems. The focus here is on the protection of fundamental rights, health, and safety. The legal framework is based on a risk-based approach: AI applications are divided into four different categories, from minimal to unacceptable risks, depending on the potential threat to society. Specifically, the AI Act provides for the following categories:
- Unacceptable Risk: AI systems that pose a threat to human rights or safety, such as those used for social scoring or manipulative practices, are prohibited.
- High Risk: These systems are heavily regulated and include applications in critical areas such as biometric identification, healthcare, transportation, education, and employment. Businesses using high-risk AI must meet strict compliance standards.
- Limited Risk: These systems face fewer restrictions but must still adhere to transparency requirements. For example, chatbots need to inform users that they are interacting with AI.
- Minimal or No Risk: The least regulated category includes AI applications such as spam filters or AI-driven video games.
The AI Act is of great importance for companies, as the new requirements not only entail compliance obligations, but also open up opportunities to gain competitive advantages.
By adapting to the legal requirements at an early stage, companies can strengthen trust among customers and partners, minimize risks, and promote innovation responsibly. A sound understanding of regulation enables them to make strategic use of the legal framework and position themselves better in international comparison.
Hence, for businesses operating in or with the EU, compliance with the AI Act will be a decisive factor. Failure to comply could result in significant penalties—up to 7% of the global annual turnover or €35 million, whichever is higher.
As the legislation moves gradually forward, it is recommended that companies, as a first step, review their AI tools and analyze how these systems are classified and regulated under the new framework to implement the necessary obligations.
From a Data Warehousing perspective: How can an AI-Mart help?
As businesses prepare to comply with the European Union’s AI Act, ensuring that their data and AI systems meet the new regulations is critical. Central to this is the concept of data governance and traceability, especially for AI models classified as high-risk. A modern data warehouse (DWH), particularly one powered by Data Vault 2.0, when combined with a specialized AI-Mart, can provide the technical foundation needed for compliance by managing the data lifecycle, ensuring transparent operations, and logging AI model activities. Data Vault 2.0 offers several advantages for this purpose, including its ability to support agile development, enabling rapid changes in business requirements; ensuring scalability, allowing businesses to handle increasing data volumes seamlessly; and providing strong historical tracking through its architecture, which facilitates easier auditing and compliance verification.
In the context of AI, the AI-Mart is a specialized data mart within a DWH, focused solely on managing AI training data. Its purpose is to provide a structured and compliant environment for storing and curating datasets that will be used to train, validate, and test AI models. Unlike a traditional data mart, the AI-Mart is designed with features tailored for AI, such as enhanced metadata, tracking, and model training documentation.
Key Features of an AI-Mart
- Data Curation for AI Training: The AI-Mart stores data specifically curated for training AI models, ensuring that all datasets are clean, unbiased, and high-quality. Built-in data governance rules ensure that only validated data enters the mart. This ensures compliance with the AI Act’s requirements for high-risk AI systems, where data must be trustworthy, accurate, and free of bias.
- Metadata and Documentation: The AI-Mart stores metadata about each dataset, including its source, transformations applied, and its use in specific AI models. This metadata is essential for traceability, ensuring that every data point used in an AI model can be traced back to its origin and all changes can be documented.
- Data Versioning and Lineage: In AI applications, ensuring that models use up-to-date and reliable data is critical. The AI-Mart supports data versioning, allowing teams to maintain multiple versions of datasets and trace changes over time. Data lineage tracking ensures that the lifecycle of the data—from ingestion to usage in AI models—can be fully traced, providing a comprehensive audit trail required for compliance with the AI Act.
This is why a robust data governance framework is crucial for ensuring compliance with the AI Act. By integrating a data warehouse (DWH) with an AI-Mart, businesses can implement stringent governance measures that ensure the quality and reliability of AI training data. For example, automated validation pipelines within the DWH verify that only data meeting predefined quality standards is used, minimizing errors, biases, and missing information. This is particularly important for high-risk AI applications, such as those in biometric identification or healthcare, where poor data quality could lead to harmful or inaccurate outcomes.
To comply with the AI Act, businesses must ensure traceability in their AI systems by tracking and documenting key stages of the AI process, from data preparation to model usage. Integrating AI model logs into a data warehouse (DWH) plays a crucial role in this, providing a centralized system to monitor and store critical information about how AI models operate and interact with data.
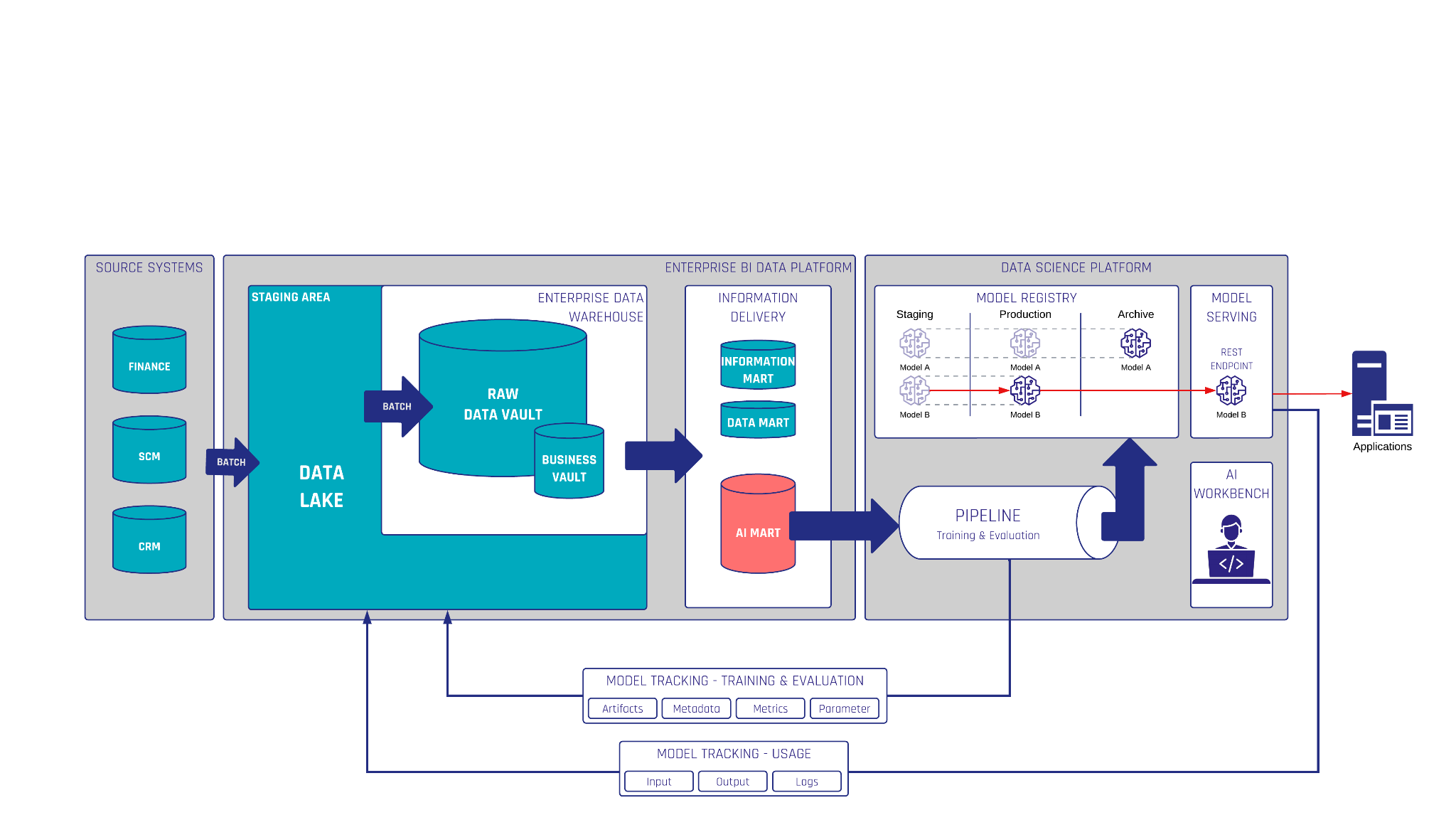
Logging AI Decisions and Outputs: Each time an AI model processes data, logs should be automatically generated and stored in the DWH. These logs capture essential details, including input data, feature transformations, model parameters, decision thresholds, and output probabilities. By loading these logs into the DWH, businesses create a detailed audit trail of AI activity, ensuring that key aspects of the model’s operations are documented.
Log Aggregation and Storage: Logs from AI models, whether during training or production, can be continuously fed into the DWH as part of the AI-Mart infrastructure. These logs may include:
- Model training logs: Documenting how the model was trained, the datasets used, and the parameters adjusted during training.
- Model inference logs: Recording the input data, features generated, and each prediction made by the model.
- Performance metrics: Storing evaluations like accuracy, precision, and recall, which help track the model’s performance over time and detect any model drift.
By storing these logs in the DWH, businesses can establish detailed records of AI model operations for regulatory purposes.
Querying and Auditing Logs: The DWH’s querying tools allow compliance teams to generate reports that show how models operate, what data was used, and how the AI model has evolved. This simplifies the process of responding to regulatory audits and demonstrates adherence to the AI Act’s requirements.
By combining a DWH with an AI-Mart for AI training data and loading AI model logs into the same infrastructure, businesses can build a comprehensive framework for compliance with the AI Act. This approach supports data governance, ensuring high-quality data for AI models, and ensures traceability, allowing businesses to track and audit every aspect of their AI systems. This not only meets regulatory requirements but also fosters trust and accountability in the use of AI technology.
Upcoming Resources and Events
- English Webinar: Join our upcoming session on “AI Act Insights: Ensuring Responsible AI for your Business” November 26th, 2024, 2pm CET
- German Webinar: Join our upcoming session on “AI Act im Fokus: Regulierung und Chancen für Unternehmen” November 27th, 2024, 2pm CET
- English Whitepaper: Preparing for the AI Act: A Practical Checklist
- German Whitepaper: Vorbereitung auf den AI Act: Eine Checkliste
For more information, contact our team at [email protected].
Final Remarks from the Authors
The AI Act should not only be seen as a regulatory challenge but also as an opportunity for businesses to differentiate themselves by adopting trustworthy and ethical AI practices. As AI continues to evolve, businesses that prioritize compliance, transparency, and human oversight will be better positioned to thrive in the coming years. By taking proactive steps now to ensure compliance, businesses can turn AI regulation into a strategic advantage, building trust with customers, partners, and regulators alike.
– Ulf Mattern (Scalefree) & Dr. Céline Helmschrot (GÖHMANN Rechtsanwälte)
