Agile Development in Data Warehousing: Initial Situation
Agile methodologies bring flexibility and adaptability to data warehousing, making them a natural fit for modern approaches like Data Vault 2.0. A common issue in data warehousing projects is that a scope is often missing and many of the processes such as controlled access, GDPR handling, auditability, documentation and infrastructure are not optimized. Additionally, data warehouse projects that have a scope often begin without a real focus on business value. This is mostly due to the fact that the use cases are not clearly communicated and the data architects do not know where to start. The consequence of this means no business value can be delivered.
Data Vault 2.0 Methodology
It is often assumed that Data Vault 2.0 is only a modeling technique, but this is not correct. Data Vault 2.0 includes the modeling technique, a reference architecture and the methodology. The methodology introduces project management tools such as CMMI, Six Sigma and Scrum to solve the problems described. While CMMI and Six Sigma deal with general project management issues, Scrum is mostly used specifically in the development team and provides the framework for a continuously improving development process. The use of agile development in Data Vault 2.0 projects will be described in more detail below.
The Scope of a Sprint
The first step in setting up a data warehouse project in an agile way is defining the objective of the project with just one or two pages. Unlike waterfall projects, the goal is to produce working pieces of usable outputs, could be reports or dashboards, in continuous iterations, otherwise called sprints. This means that we don’t need to plan the entire project in detail but instead can build around a general idea or goal for the final data warehouse before then focusing on planning the first sprints. In order to address the aforementioned problems, the focus of the sprints needs to be centered around business value. For this reason, it is important to receive constant feedback from the business users for a continuous improvement process.
Define the project
Both the scope of a sprint and the architecture follow a business value driven approach built vertically and not horizontally. This means they are not built layer by layer but instead feature by feature. A common approach for this is the Tracer Bullet approach. Based on business value, which is defined by a report, a dashboard or an information mart, the source data will be identified and modeled through all layers and loaded.
As shown in Figure 1, the entire staging area layer is not initially built but rather a small part of the respective layer is built based on data in the scope, in this case the SalesReport.
Agile Development
Before new functionality can be implemented in a sprint, it needs to be defined.
This task lies with the product owner as they are the ones to write and prioritize user stories.
As already explained, the goal of a sprint is to produce working pieces of usable outputs called features.
In addition, there are tech topics that need to be considered. There are various methods to support Sprint Planning, such as planning poker or Function Point Analysis, which are discussed in more detail in another article.
Another good indicator is to evaluate the sprint itself while the sprint is still ongoing. If the development team does not manage to implement a feature in a sprint, this can often be seen as a good indicator that the scope is too large.
To avoid this, all work packages that are not relevant for the feature should be removed. Though, what is often the case these work packages are not completely removed out of fear from the business user.
To address this fear it is important to educate the business user that they will be delivered but only in a later sprint and temporarily moved into the backlog.
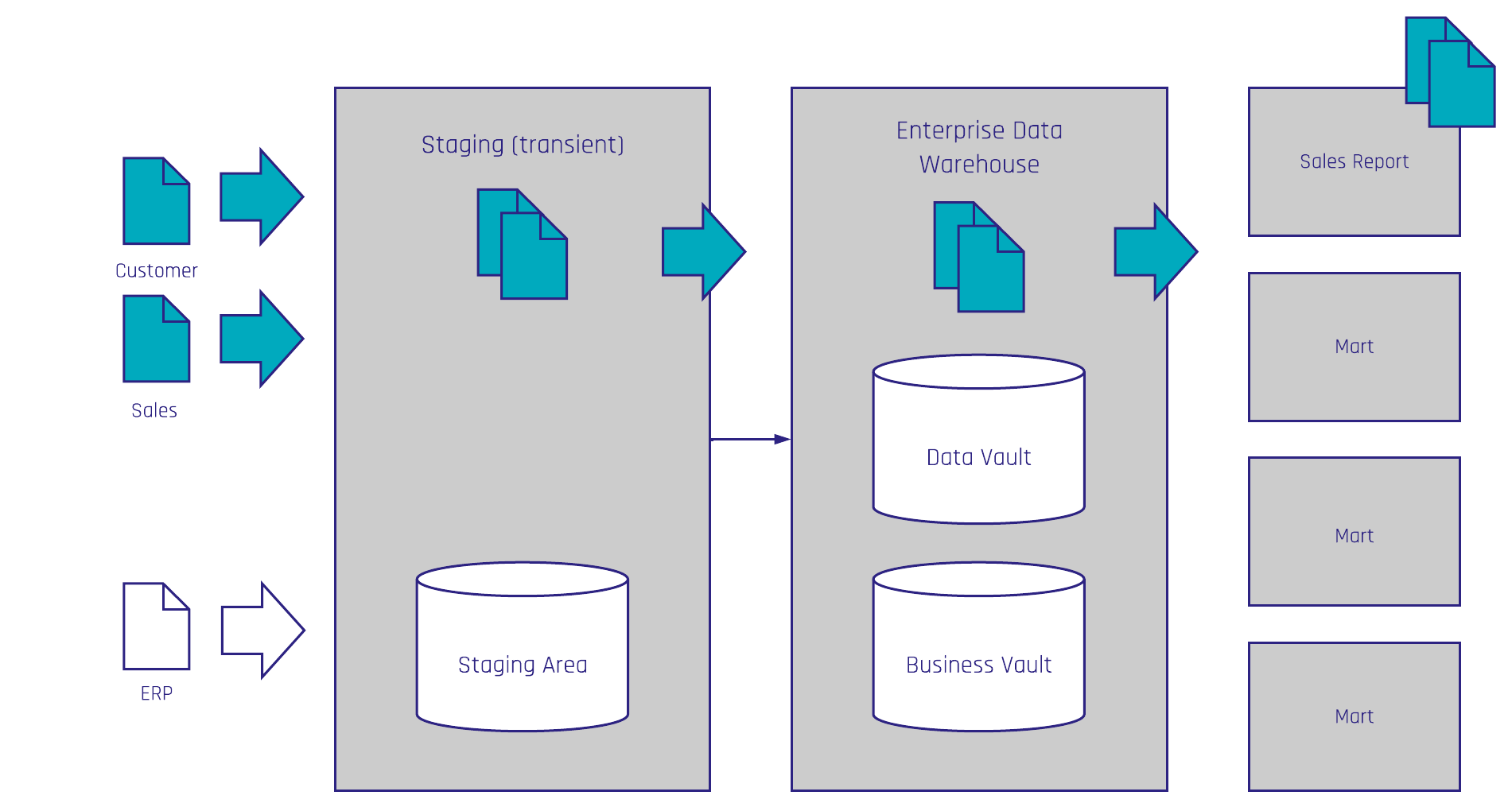
Due to the flexible and scalable Data Vault model, these layers can be extended with the next feature with little to no re-engineering. This is possible due to the fact Data Vault consists of a Raw Data Vault and a Business Vault model which means it contains the logical architecture as well as the data modeling perspective. The Raw Data Vault is modeled in a data-driven way by integrating the data by business keys. Only hard business rules like data type conversions or hash key calculations are applied. All other soft business rules are only applied in the Business Vault.
Here, we turn data into information. For this reason, the Raw Data Vault requires less refactoring and can be extended limitlessly.
Agile Development Review
Another important success factor for agile projects is proper review and improvement. Even before the next sprint starts, two meetings must be held by the team:
- The sprint review meeting: This meeting is about reviewing the delivered features. Usually the development team, the product owner, the Scrum Master and the end-users participate in this meeting.
- Retrospective meeting: This meeting usually takes place directly after the review meeting and focuses on identifying activities that need to be improved.
- Backlog refinement for prioritizing the user stories and to make sure that the team understands what to do
- Sprint planning to plan which user stories fit into the next sprint based on estimating the effort.
It is important that these meetings are held so that toe source errors can be found. In this way, the outcome of a project can be improved and the development processes optimized in an iterative way.
Conclusion
Data Vault 2.0 is not only a scalable and flexible modeling technique, but a complete methodology to accomplish enterprise vision in Data Warehousing and Information Delivery by following an agile approach and focusing on business value. By using agile methods in data warehousing, the focus in projects can be on the business value and delivering useful products to the customer.

